Most PMOs recognise know that demand management is time-consuming and complex. But we also all know it is central to the business strategy. Here’s our take. Read why having a demand manager on your PMO is beneficial to your organisation.
What is Demand Management?
Demand management (DM) is a planning methodology that helps you predict, manage, and plan the demand for products and/or services. An organisation will implement a DM methodology to generate new ideas, and identify new projects that align with strategic objectives.
DM is about striking the balance between the new and the old. Innovation and adaptability are critical to business success. A DM allows businesses to adapt to changing circumstances while utilising their resources effectively.
The output of demand management should work to assist the organisation in selecting and prioritising its portfolio. The process should enable the organisation to capture its strategic commitment, and reflect that in ongoing activities.
Why is a Demand Manager Important for your Organisation?
When done right, having a demand manager can become a secret weapon for your business decision-making process.
In the business world, we often talk about ‘opportunity cost’. A demand manager holds the essential role to ensure your opportunity cost pays off. They will gather, analyse, and make informed decisions on which options are most viable, given the organisation’s limited resources. A demand manager is realistic about your business’ capabilities, balances the opportunity costs, and achieves the best outcome.
A demand manager is more than just a tool, but can also be a critical factor for success in your portfolio.
Where a Demand Manager fits in a PMO
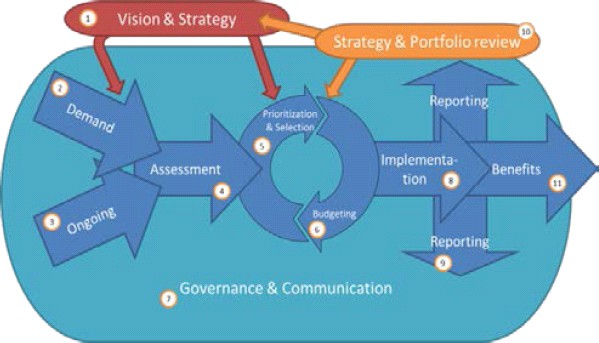
As we can see from the above diagram, DM is the second step within the portfolio management process and thus holds a very critical position. A demand manager informs the PMO of overarching strategy, and is one of the PMO members who select and enact projects.
Though the demand manager is usually focused internally, they also should take into account external factors, such as the general strategy of the organisation and the overall market situation.
They can evaluate proposed ideas and projects by their alignment with the strategic direction of the organisation, and the activities that are currently in the pipeline.
What is an Example of Demand Management?
As a planning methodology that helps to predict, manage and plan the demand for products and services, DM can be used at both macro and micro levels.
At the macro level, a demand manager would be concerned with the financial regulation of money markets by the government by setting interest rates. They could use this information to predict how this would influence their customers’ buying habits.
On the other hand, at the micro-level, a demand manager working for a cellular provider may suggest the company reduce demand during peak hours by providing free weekend and night use.
Components of Demand Management
The Business Case
First is the business case (BC). The key point about the business case is its structure needs to reflect the demand management process.
Budget
Budgeting is the process that defines and approves the number of resources available. From there, a demand manager can determine the feasibility of their demand management strategy, and how best to implement it with the available resources.
Component and Project Selection
The next step for a demand manager is to prioritise the components of their demand strategy. A major factor that plays a part here is the alignment of components with the general strategic direction of the organisation. Demand managers should have this same focus on strategic alignment when choosing the projects to commence.
Portfolio governance
After the demand manager completes the business case, budget, and component and project selection, they can start working on portfolio governance. This task primarily defines the chain of accountability, responsibilities, and roles. This part of the process also helps to define reporting and communication.
Portfolio Implementation
From the above steps, a demand manager can construct a clear and comprehensive draft of the portfolio. This portfolio and a portfolio implementation plan should be passed onto the appropriate executive for approval. After this, the PMO can start to implement the portfolio and monitor its progress.
Portfolio Reporting and Reflection
As the portfolio is implemented, more teams are involved. Project managers are responsible for completing actionable tasks that make up the various projects. Ideally, the project managers will keep tabs on project progress and reporting, and they will pass this data onto the PMO.
The PMO can evaluate the project, program or operation status, and the status of the whole portfolio. This step in the process also reports the success and achievement of the strategic objectives, and manages the benefits produced.
It is important for the PMO to reflect on the strategy and portfolio through its implementation. This includes assessing the relevance of the strategy in the current market conditions. In addition, consider the benefits realisation component. Has this strategy yielded a positive or negative benefit for the business?
Best Practices for a Demand Manager
In order to have effective demand management, here are a few tips to follow:
1. Effective Demand Management needs transparency
It is vital that all your key suppliers have a transparent idea of your predicted demand. This will help them secure inventory in a timely response in accordance with your demand projections. As a result, you will be able to better respond to customer demand.
2. Effective Demand Management engages with alternate sources of supply
If you have multiple sources of supply, make sure that you are always in touch with your secondary supply sources. If you do not have secondary sources, make sure to explore potential opportunities to make your demand management a smoother process.
3. Effective Demand Management constantly updates inventory policy and planning
It is vital to update your inventory policy and planning. There should be regular updates in the policy and planning in accordance with the changing market conditions. This will ensure that the business remains agile and flexible to changing patterns in demand. Moreover, there should also be plans and policies in place for uncertain situations such as a pandemic.
4. Effective Demand Management is always aligned with supply management
Having proper demand management alone will not do the job for you. What an organisation needs is properly aligned demand and supply management so that there can be quick adjustments made if there are disruptions in either.
pmo365 and Demand Management
Demand management can be greatly simplified and streamlined when you use smart tools. When you implement an intuitive PPM solution such as pmo365, you can leverage the advanced portfolio analysis tool, integrative capabilities, and the accurate information it provides for effective demand management.
Because of its ability to automate reports and offer real-time insights, organisations can rely on pmo365 as their single source of truth, making demand management more efficient and precise.
Take advantage of a free trial with our PPM experts today to see firsthand how pmo365 streamlines demand management processes and drives better decision-making













