While risk management isn’t a new concept, it holds increasing importance in our increasingly complex market. New tools make managing risks easier, but we haven’t eliminated the role of competent project managers in monitoring risks. Therefore, the question remains: how to monitor risks in project management?
In this blog post, we will explore the definition of risk management and its benefits. More importantly, we’ll discuss how to monitor risks in project management effectively, and what processes and tools you can employ to do this.
What is risk management?
The Project Management Institute defines risk management as: ‘the art and science of identifying, analysing, and responding to risk factors throughout the life of a project and in the best interests of its objectives.’
This highlights an underpinning principle: risk management is not a reactive practice. In contrast, it is a proactive practice that identifies and plans for different risks before they occur.
How your organisation manages risks, or should manage risks, will vary. Ultimately, your risk management practices will depend on the type of projects you are running. Thus, practices can range from highly detailed mitigation plans to simple risk prioritisation charts- it just depends on the size and complexity of your projects.
Before diving any further into risk management, let’s clarify the difference between a risk and an issue.
Risks vs Issues
Here is the key distinction between the two:
- A project risk is anything that could impact the success of a project. This could be by impacting the project timeline, budget, or performance.
- A project issue is anything that has already impacted the success of a project. Therefore, solving issues is a reactive practice, rather than proactive one.
When you identify potential issues that can impact the success of a project, you’re identifying risks. Effective risk management will address these risks, and stop them progressing into an issue. These project management practices protect the success of projects.
Benefits of monitoring risks in project management
There are plenty of benefits of effective risk management, many on an organisational-wide scale. These include:
Identifying hidden risks
When you undertake risk management, the early stages often revolve around identifying risks which may not be immediately obvious. As your organisation establishes an effective risk management process, your teams will be able to tap into historic data to identify risk patterns. This will further increase your ability to identify ‘hidden risks’ that otherwise could go unaddressed.
Gaining visibility and control over project risks
Only once you can see the potential problem can you effectively address the problem. Therefore, risk management increases the visibility of organisations. In turn, this enables them to have an accurate understanding of the risks within their project portfolios.
In turn, this allows them to manoeuvre the organisation to holistically better position. Without enterprise-wide visibility of risks, organisations risk losing the opportunity to shift resources to effectively address risks. To read more about how to manage potential risks, check out this article.
Improve stakeholder management and expectations
As project managers, we know the best way to manage expectations is by keeping everyone on the same page. This applies to risk management as well. When you have effective risk reporting and analysis tools, information can be clarified and prioritised. This ensures teams relay the most relevant and accurate information to stakeholders so they can be addressed promptly.
Increase the likelihood of project and organisational success
By identifying, prioritising, managing, and mitigating risks, you reduce the problems that jeopardise a project’s success. However, neglecting to manage risks effectively doesn’t only damage projects. Research shows that unmanaged risk events can negatively impact overall employee productivity, operational efficiency, employee safety, competitive differentiation, and reputation. Risk management is thus a critical tool to ensure organisational success beyond the realm of projects alone.
Different types of risks
Risks come in all different shapes and forms depending on the type of project. However, several common types of risks affect three core areas of projects – cost, schedule, and performance.
- Cost-related risks
These are risks that can impact the project budget, typically causing the project to run over budget. Things such as inaccurate cost estimation and external supplier cost increases are common cost-related risks.
- Schedule-related risks
These are risks that can lead to schedule delays and overall project delays. This is commonly caused by unaccounted scheduling conflicts or scope creep.
- Performance-related risks
These are risks that will prevent teams from producing consistent results. These are typically internal risks related to internal processes, structures, or resources limitations. As a result of these risks, teams can be restricted or delayed in achieving results.
It’s important to remember not all risks are equal- each risk will have a different severity on the project. Similarly, not all risks are negative. An unexpected event can either positively or negatively impact a project. In the same way, project risks can be both positive and negative.
- Negative risks
These are risks that can harm the project or the organisation as a whole. Unsurprisingly, the risk management processes aim to reduce, mitigate, or prevent these risks.
- Positive risks
These are unaccounted events outside the organisation’s control that can positively impact the project or organisation. For example, a supplier delivers products earlier than expected, causing the project to be ahead of schedule.
While risk management is primarily focused on addressing negative risks, it’s important to prepare for both positive and negative risks. This ensures teams act on the most accurate estimations and understandings of their project context, and respond accordingly. A positive risk can be wasted if teams are not prepared to reap its benefits.
7 steps of how to monitor risks in project management
Every project, team, and organisation will have unique risk management processes. However, there are some underpinning steps which most organisations implement into their risk management activities. These are seven steps in the risk management process:
1. Identify the risks
Identifying risks is the first step, as it allows teams to evaluate and mitigate risks. Project teams and managers can ask themselves questions to guide this process. Some critical questions to ask include:
- What areas of the project are vague or vulnerable?
- What risks have occurred in previous projects that can also occur here?
Teams can identify risks by conducting stakeholder interviews, team workshops, SWOT analyses, assumption identification, and risk analysis assessments. Teams must identify the root causes of risks during this process to ensure their risk response is truly effective.
2. Analyse the risks
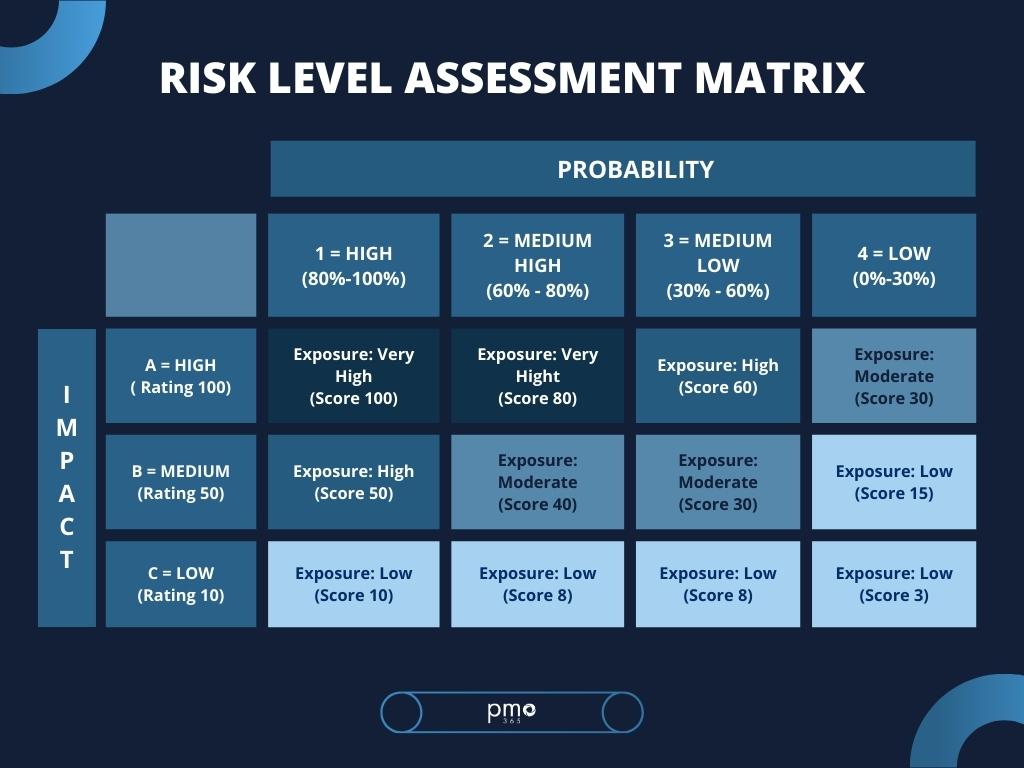
The next step is to then analyse the likelihood of the risk occurring, its severity, and the necessary response towards it. We can easily evaluate this through a risk level assessment matrix. The matrix shown below considers two factors:
i) Measuring the probability of the risk occurring and
ii) Evaluating the level of impact it has on overall project success.
- Probability of risk occurring:
- High probability (80% ≤ x ≤ 100%)
- Medium-high probability (60% ≤ x)
- Medium-low probability (30% ≤ x)
- Low probability (30% ≥ x)
- Level of risk impact:
- High: catastrophic (rating A – 100)
- Medium: critical (rating B – 50)
- Low: marginal (rating C – 10)
3. Prioritise risks
Once the risk level and exposure of each risk have been identified, the team can prioritise the right risks. In this case, the most severe is most likely to be placed the highest on the risk priority register. With the help of project management software, risk levels, and exposure can be calculated in real-time to help inform your risk prioritisation needs. You can use a risk breakdown structure to help with this step.
4. Assign risks
The next step is to then assign the risk to the right people. Risk allocation is particularly important in complex projects, as risks may be interconnected, or require the technical skills of specific people. In those situations, assigning a risk owner ensures someone is managing volatile risks which require continual monitoring. You may be familiar with how project management software streamlines this process, as you can manage risk ownership and communication within the application itself.
5. Monitor and report on risks
Once your project is up and running, the team should continually monitor project risks to avoid any unexpected risks. Project management software is particularly handy in these situations as they allow you to easily keep track of risks in real-time. In addition, many have reporting features which ensure teams build the right reports to send to the necessary stakeholders.
Conducting regular status updates keeps your team and all relevant stakeholders on the same page. By doing this, your team can effectively react to changes and pre-emptively prepare for potential risks. In addition, effective risk management relies on a culture of collaboration. Such a culture encourages team member contribution, and assures them that their insights of potential risks are valued.
6. Respond to risks
This is when you put your contingency plans into action. If your team has developed robust response or contingency plans, then teams will know exactly what to do when risks emerge. This allows teams to respond to changes as quickly and effectively as possible. In an increasingly fast-paced market, it is essential to swiftly address risks as they emerge.
7. Improve risk management processes
Always look the improve your processes. Reviewing risk management activities at the end of each project allows teams to identify opportunities for improvement. You can collate this evaluation in a lessons learnt document, which your team can use to inform future risk management activities. Risk management is a continual process, so such reviews ensure your teams are always improving and adapting their processes.
Risk management tools
There are various tools which you can use to conduct risk management activities accurately and effectively. Many of these tools are already integrated into project management software, so you may already have access to them. Teams can now easily tap into real-time data, automation capabilities, and high-level calculations that will improve their risk management activities. Some key risk management tools include:
RAID logs
RAID logs are risk management tools that allow teams to log and track risks, assumptions, issues, and decisions (thus, the acronym). In addition, RAID logs ask assumptions, issues and dependencies related to a project, thus earning its short form RAID. These logs give teams greater visibility and control over risks, as all risk related factors are already listed. This simplifies the risk management process and streamlines reporting activities. RAID log software often includes a heat map which identifies the most pressing risks to be addressed.
Risk Breakdown Structure
Risk breakdown structure (RBS) is another risk management tool that organises potential risk sources into a hierarchical framework. RBS typically use scoring systems to identify high-level risks. This enables teams to prioritise addressing the right risks. They give project managers greater visibility over planned and unforeseen risks, therefore reducing the impact of risks project success. A RBS may utilise a risk assessment matrix, and can be used in tandem with a risk register to define proceeding risk management actions.
Risk Register
A risk register is a document that collates all the identified risks, their consequences, team responses, and ownership of those problems. The risk register allows teams to have a clear understanding of all risk-related activities and processes. As a result, a team can promptly address risks and escalating issues with minimal disruption. A risk register will consist of different parts that clarify all risk management needs. It will typically feature an outline of risk response plans, ownership of the risk, ‘levels’ of risk escalation, and triggers.
Risk Repository
A risk repository is a comprehensive collection of all risk events identified throughout the organisation thus far. It aims to improve the risk management processes across the organisation by acting as a central repository. A risk repository is especially beneficial for teams who are looking to improve their risk management practices.
Take your risk management activities to the next level with pmo365
With our intuitive RAID logs and integrative system, pmo365 consolidates all your project-related activities across your organisation onto a single platform. This ensures you always have real-time, accurate data informing your risk management actions. To learn how, see our tool in action with our free trial. If you want to learn more tips on how to level up your risk and project management activities, check out our blog!